Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /var/www/vhosts/gestortectic.com/mesa.gestortectic.com/wp-content/plugins/fulltext-search/includes/wpfts_querylog.php on line 520
Last Updated: 19/06/2023
Plasmodium ovale hypnozoite development and relapse: a coordinated in vivo in vitro study
Objectives
To examine in vivo relapse phenotypes for P. ovale curtisi and P. ovale wallikeri as well as directly measuring hypnozoite commitment in vitro.
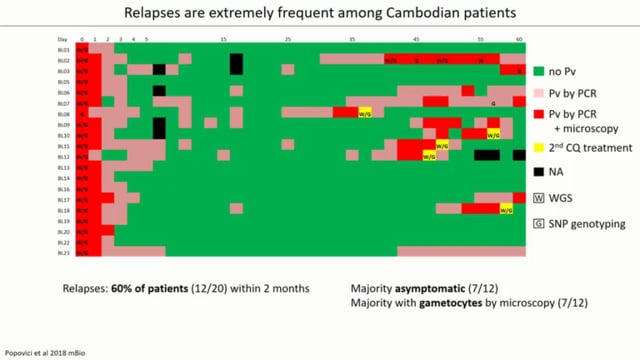
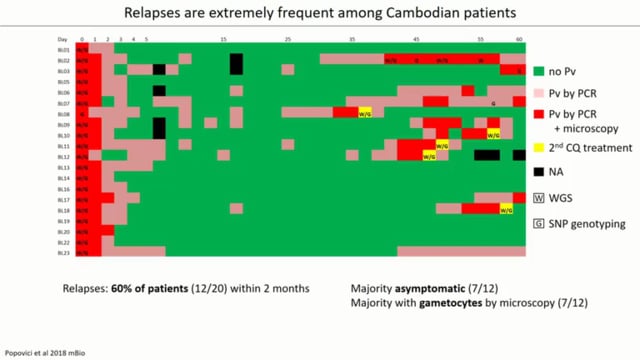
Malaria control interventions focused on P. falciparum are not adequate to address the growing burden of non- falciparum species, especially those malaria species that cause relapse. Plasmodium ovale, like P. vivax, causes recurrent infections arising from hypnozoites in the liver. Hypnozoites “sleeping” in the liver before they reactivate to cause relapse are invisible to malaria diagnostics and impervious to first-line ACT regimens. Thus they likely play a key role in the rising number of P. ovale cases across Africa, estimated to exceed 15 million cases each year. Almost nothing is known about P. ovale hypnozoites and their relapse patterns. It has only been recently known that P. ovale in fact comprises two non-recombining species – P. ovale curtisi and P. ovale wallikeri. Interestingly, these two species may exhibit distinct relapse patterns, suggesting species- specific hypnozoite biology. However, the little evidence available regarding the two species’ relapse patterns is confusing: epidemiologic data in travelers suggest that P.o. wallikeri relapses occur at shorter intervals, but the first prospective study of P. ovale in Africa only found relapses due to P.o. curtisi, not wallikeri. The hypothesis is that both P. ovale curtisi and wallikeri develop hypnozoites and relapse in a species-specific manner. To test the hypothesis, tools built to study P. vivax will be deployed. Using targeted sequencing methods designed to distinguish relapses from re-infections in endemic settings developed by investigators at the University of North Carolina, and a state-of-the-art 384-well primary human hepatocyte platform for studying Plasmodium liver stages developed at the University of South Florida, the team will 1) Conduct an observational cohort study to define species-specific relapse rates of P.o. curtisi and wallikeri and 2) Establish a liver stage model for P. ovale to evaluate hypnozoite commitment in both species. The fieldwork for this proposal will be conducted within the framework of a larger R01-funded malaria transmission study in Bagamoyo, Tanzania. This will allow the project to leverage the significant molecular and entomologic capacity that have been developed there, where Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes have successfully been infected with P.ovale. In partnership with the Muhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences, 40 volunteers with qPCR-positive P. ovale infection will be identified and followed up every 2 weeks to genotype any recurrences that occur over 8-12 months, and conduct mosquito feeding assays to generate 15-20 P. ovale sporozoite isolates using blood-fed mosquitoes from the same volunteers. Cryopreserved infectious sporozoites will be shipped to the USF, where liver-stage experiments will be performed to measure hypnozoite commitment (the ratio of developing schizonts to small-form hypnozoites) and to test anti- hypnozoite drugs. This study will establish the first liver-stage model of P. ovale. Findings will crucially inform the development of drugs and strategies to achieve the elimination of all malaria, not just P. falciparum.
Nov 2020 — Oct 2023
$417,602