Last Updated: 02/12/2024
Evaluation of transmission blocking efficacy of P. vivax vaccine: a collaborative study using Brazilian infected blood
Objectives
To test the transmission-blocking effect of the vivax malaria vaccine against the locally prevalent vivax malaria.
Doctor Heitor Vieira Dourado Foundation for Tropical Medicine (FMT-HVD), Brazil
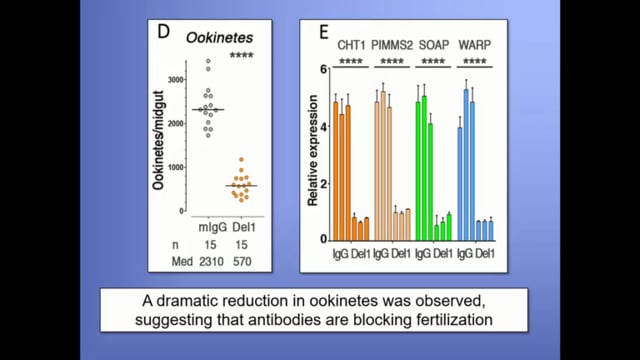
In this study, an international joint research was conducted with FMT-HVD (Research Institute for Tropical Diseases) in Manaus, Brazil, and tested the transmission-blocking effect of the vivax malaria vaccine developed by the applicant against the locally prevalent vivax malaria. Accurately assess using protozoa. Specifically, 1) Collect blood from Plasmodium vivax infected people in Brazil. 2) After mixing the blood of the infected person and the serum of the vaccinated mouse, DMFA is performed by sucking the blood of Anopheles mosquito. After 10 days, the Anopheles mosquito is dissected, the number of oocysts in the midgut is observed, and the reduction rate is used to evaluate the propagation-blocking effect (target value >90%). During the research period, the papers will be submitted and the results presented at the International Parasitological Society ICOPA and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene ASTMH.
Jan 2022 — Dec 2024
$59,064